The convergence of 3D printing and biotechnologies is at the heart of medical innovation. This technology goes beyond simply revolutionizing manufacturing processes; it is opening up new possibilities for the medical industry. From the creation of artificial organs and tissue regeneration to the design of personalized medical tools, 3D printing technology is playing a crucial role in overcoming the limitations of medicine. This article will examine the impact of the convergence of 3D printing and biotechnology on the medical industry from five perspectives.
1. Artificial Organ and Tissue Printing
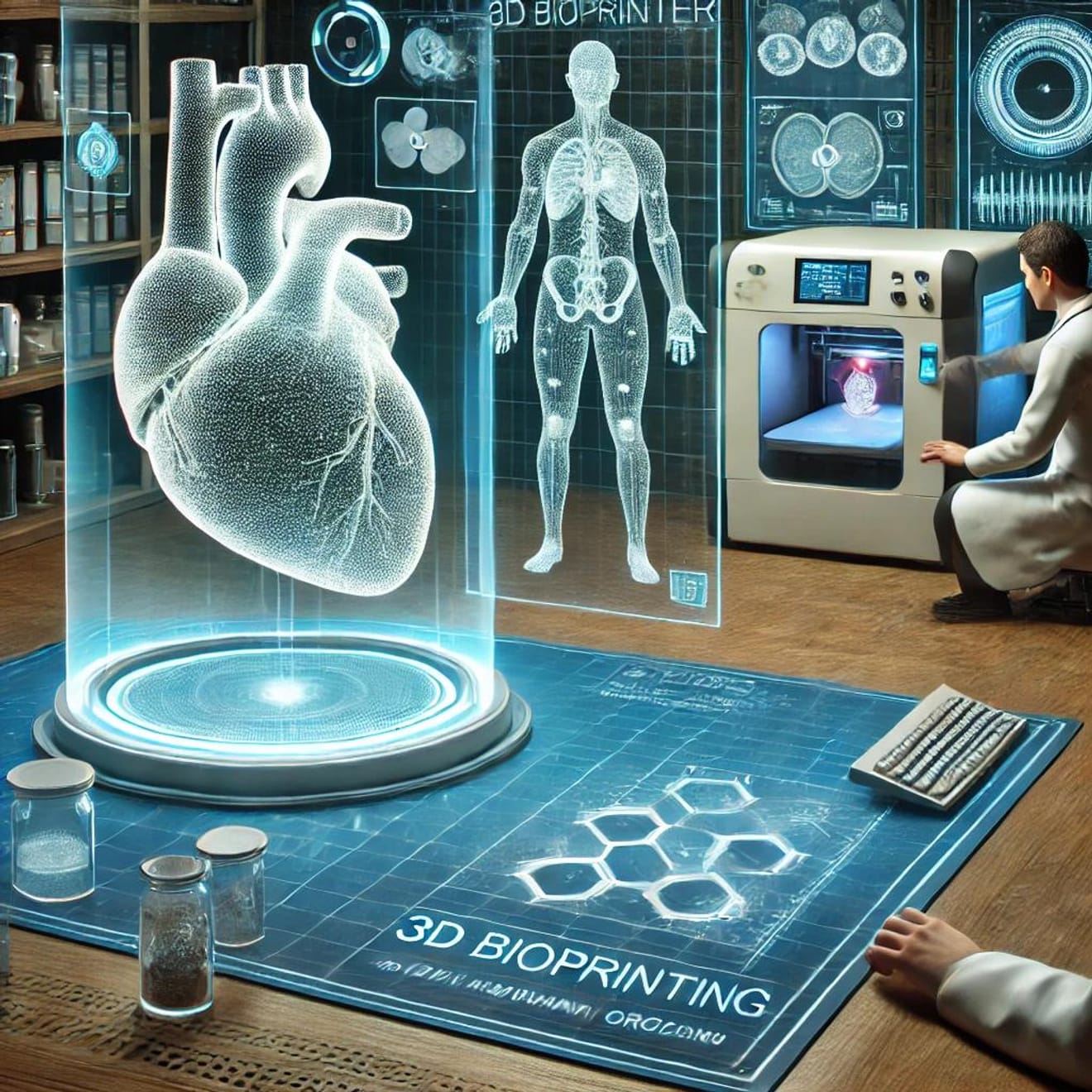
3D bioprinting is used to create artificial organs and tissues using a patient's own cells.
-Potential of Artificial Organs: Technologies for creating vital organs such as kidneys, livers, and hearts using 3D printing are constantly advancing. This offers the potential to solve the limitations of organ donation and organ transplant waiting lists.
-Tissue Regeneration: 3D printing technology is already being used to regenerate tissues such as skin, cartilage, and bone. The creation of artificial skin for burn victims is a prime example.
This technology utilizes a patient's own cells, thereby reducing the possibility of immune rejection and contributing to a higher success rate for treatments.
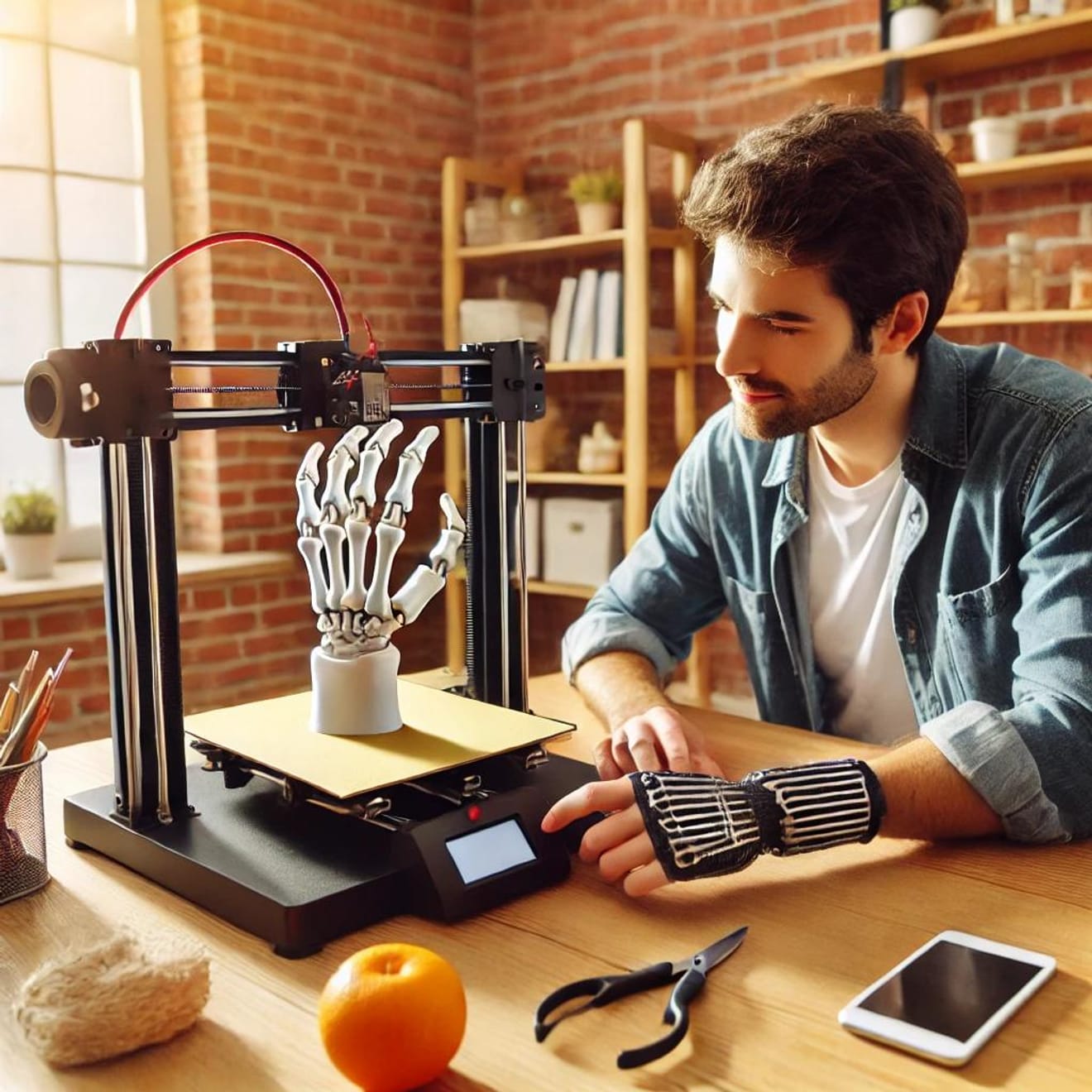
2. Customized Medical Tools and Instruments
3D printing has revolutionized the creation of customized medical tools for individual patients.
-Medical Instrument Customization: 3D printing allows for the creation of medical instruments that precisely fit a patient's anatomy. For example, personalized dental prosthetics, implants, and prosthetics are being created using 3D printing technology.
-Improved Accuracy and Efficiency: The creation of customized instruments, which was time-consuming with traditional manufacturing methods, is now faster and more precise thanks to 3D printing.
This significantly improves patient treatment outcomes and reduces recovery time.
3. Innovation in Drug Development and Delivery Systems
3D printing technology is also bringing about innovations in drug development and delivery systems.
-Personalized Drug Manufacturing: 3D printing allows for the creation of customized drugs based on a patient's condition. For example, drug dosages can be adjusted based on a particular patient's metabolic rate and genetic information.
-Drug Delivery Systems: Drug delivery devices created using 3D printing are designed to deliver medication precisely to the area where it is needed. This helps maximize the drug's effectiveness and minimize side effects.
This technology increases the efficiency of drug development and improves the patient's treatment experience.

4. Surgical Guides and Educational Materials
3D printing is also used in surgical preparation and medical education.
-Surgical Guide Creation: 3D printing can be used to create surgical guides that model a patient's anatomy. This greatly assists surgeons in planning and performing surgeries.
-Medical Educational Materials: Medical students can use 3D-printed anatomical models to receive training in a realistic environment.
This technology contributes to increased precision and success rates in surgery and improves the quality of medical education.
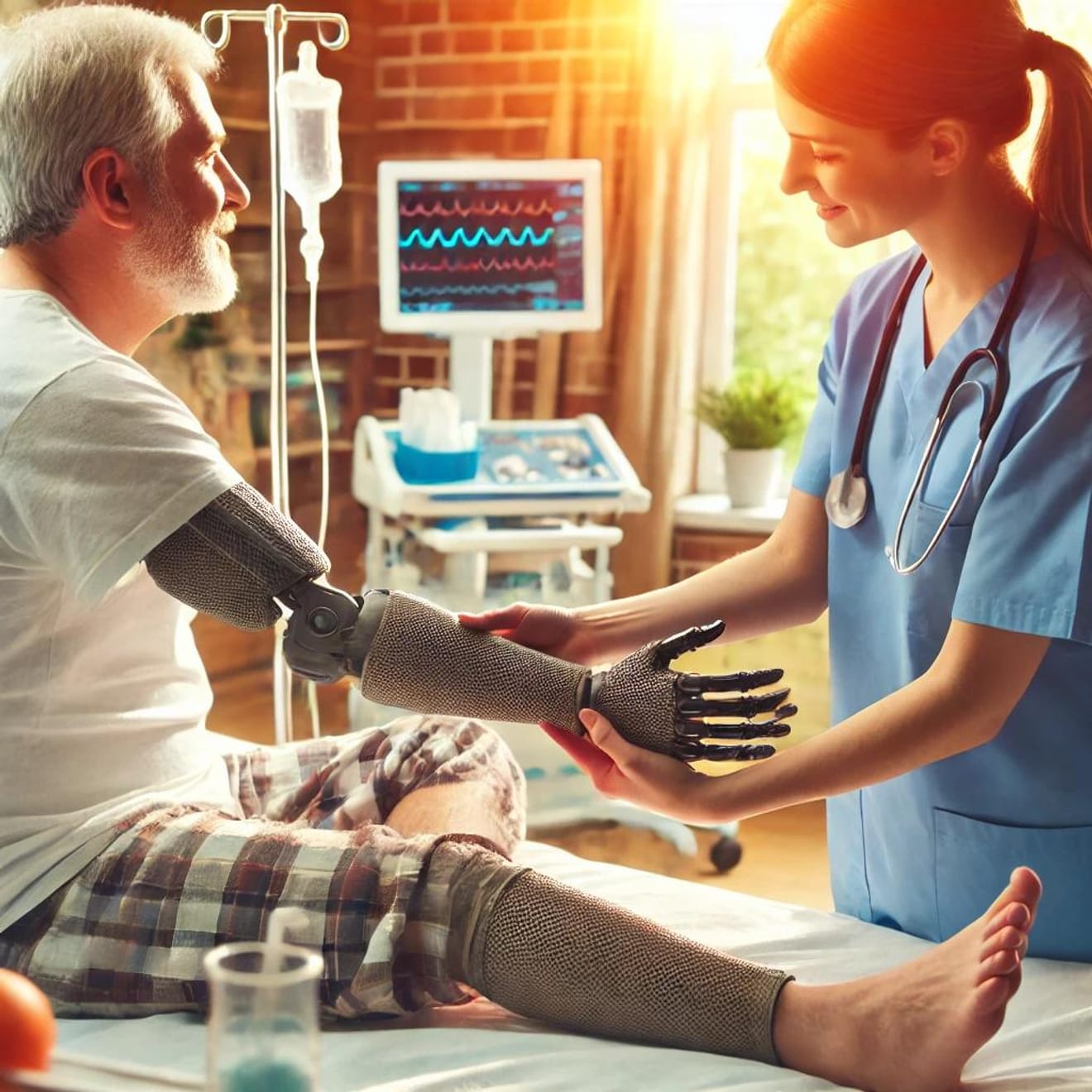
5. Cost Reduction and Improved Accessibility
3D printing technology contributes to cost reduction and improved accessibility in healthcare.
-Cost Effectiveness: By replacing traditional complex manufacturing processes, the production costs of medical equipment and instruments can be significantly reduced.
-Improved Healthcare Access: 3D printing technology offers the potential to quickly create necessary equipment and tools even in areas with limited healthcare resources.
This is creating an environment where more people worldwide can access high-quality healthcare services.

The convergence of 3D printing and biotechnology is transforming the paradigm of the medical industry. From the creation of artificial organs and tissues, the development of customized medical tools, drug manufacturing, and the creation of surgical guides and educational materials, this technology is bringing about revolutionary changes to all aspects of medicine. Furthermore, by reducing costs and improving access to healthcare, it is providing more patients worldwide with the opportunity to receive high-quality medical services. Future advancements in 3D printing and biotechnology will unlock even more possibilities, making the future of medicine brighter and healthier.
Comments0